Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Caching benchmarks#
Saving benchmarks#
Performance benchmarks as run by pyquickbench are typically quite lengthy.
While obvious for complex benchmarks, this is still true for simple benchmarks.
Indeed, by default, pyquickbench uses a strategy derived from the standard timeit.Timer.autorange() to assess the number of times a benchmark should be run to ensure reliable timings, which comes with significant overhead as any call to this function will require a (configurable) minimum execution time of 0.2 seconds.
Caching benchmarks results is a great way to reduce this overhead.
In pyquickbench, caching results in order to avoid a full re-run is as simple as providing a file name to pyquickbench.run_benchmark(). If this file does not exist, it will be created. Both *.npy and *.npz extensions are accepted.
import numpy as np
import pyquickbench
def comprehension(n):
return ['' for _ in range(n)]
def star_operator(n):
return ['']*n
def for_loop_append(n):
l = []
for _ in range(n):
l.append('')
all_funs = [
comprehension ,
star_operator ,
for_loop_append ,
]
n_bench = 12
all_sizes = [2**n for n in range(n_bench)]
timings_filename = "My_benchmark_file.npy"
all_times = pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
)
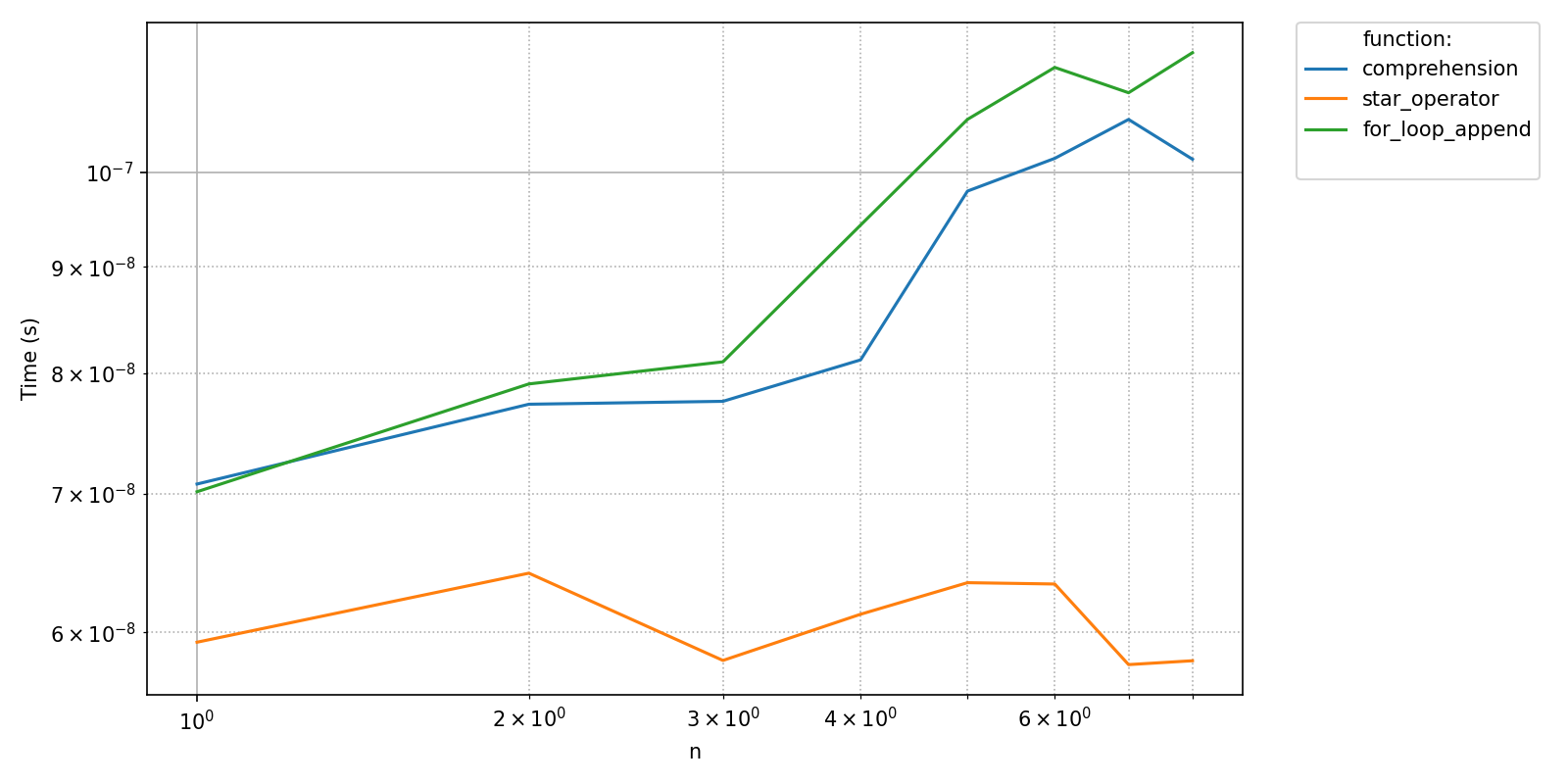
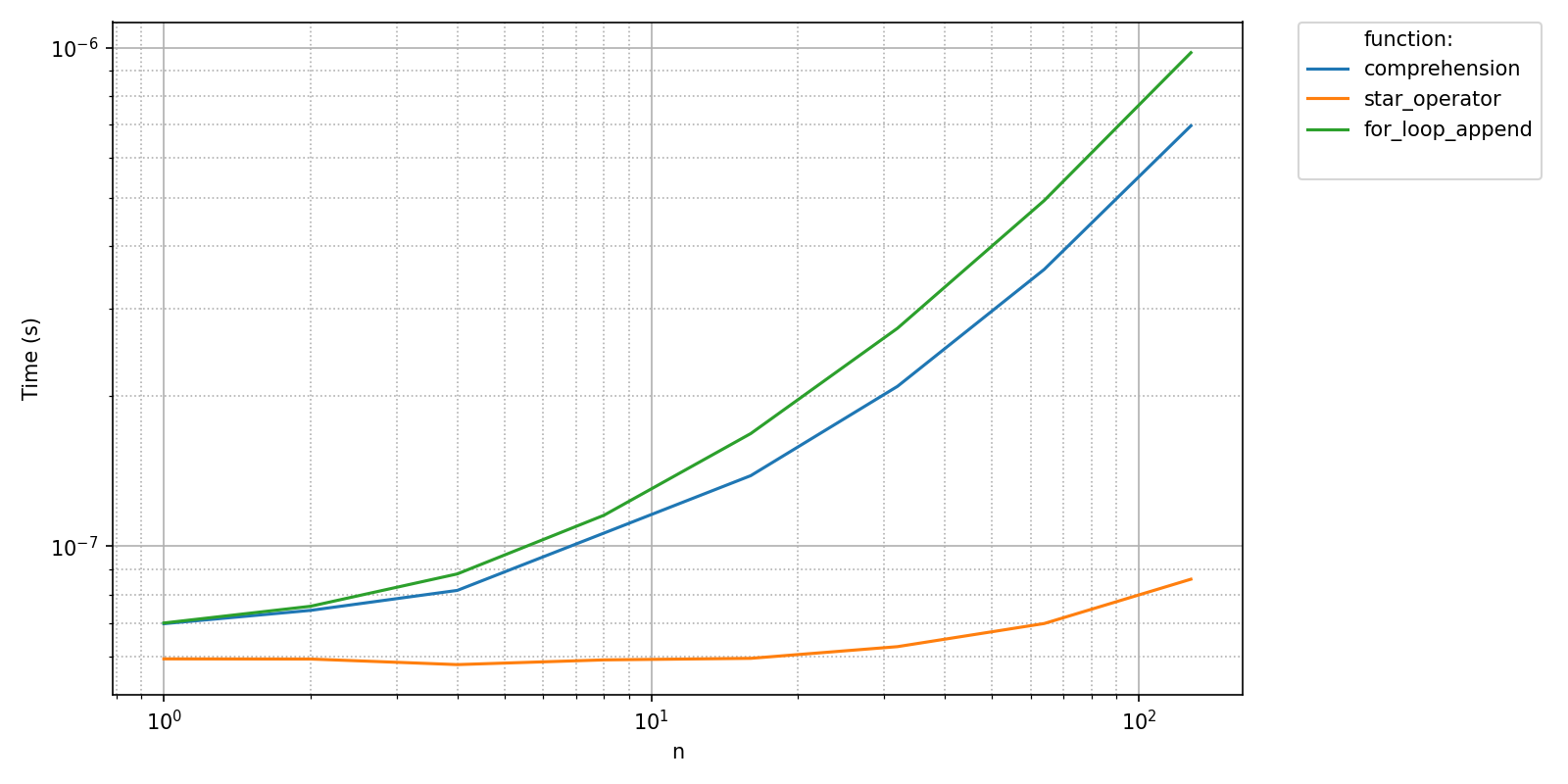
pyquickbench.plot_benchmark(
all_times ,
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
show = True ,
)
Skipping benchmarks#
Another call to pyquickbench.run_benchmark() will detect that the file exists. The benchmark will not be run the a second time, and the contents of the file is used instead.
all_times_bis = pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
)
np.all(all_times == all_times_bis)
np.True_
Forcing benchmarks#
A full re-run can nonetheless be forced if the keyword ForceBenchmark is set to True. The default value for ForceBenchmark is False.
all_times_ter = pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
ForceBenchmark = True ,
)
Detecting obselete benchmarks#
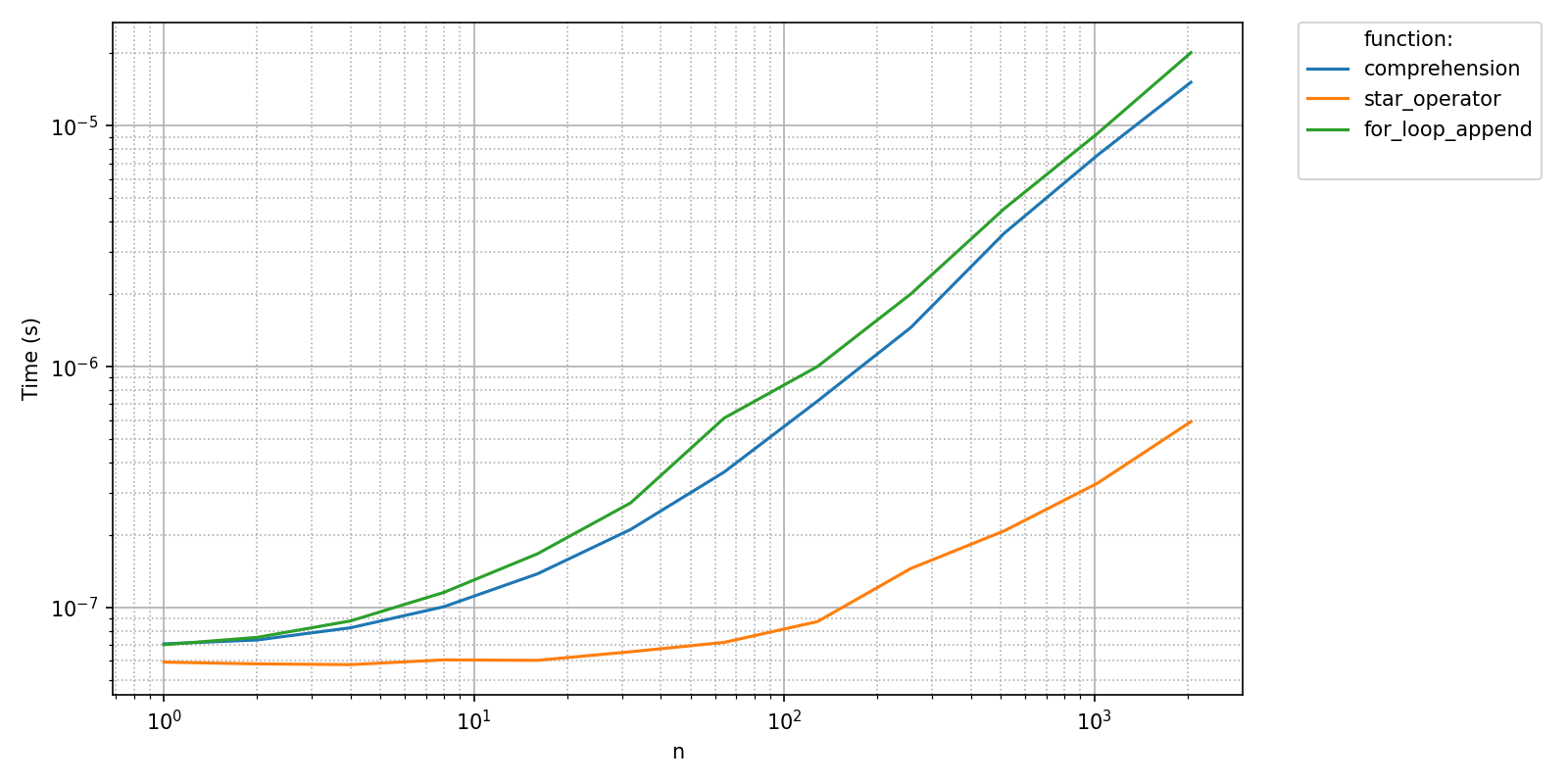
If the file on disk corresponds to a benchmark with more or fewer runs, the whole benchmark is run again, and the contents of the file is updated. For instance, the following will run the benchmark again:
n_bench = 8
all_sizes_small = [2**n for n in range(n_bench)]
all_times_small = pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes_small ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
)
pyquickbench.plot_benchmark(
all_times_small ,
all_sizes_small ,
all_funs ,
show = True ,
)
We can check that the two benchmarks have non-matching shapes.
print(f'Initial benchmark shape {all_times.shape}')
print(f'Current benchmark shape {all_times_small.shape}')
Initial benchmark shape (12, 3, 1, 1)
Current benchmark shape (8, 3, 1, 1)
This mechanism can easily be tricked as it only checks for array dimensions and not content. Indeed, all_sizes is not stored in the *.npy benchmark file, and the test only relies on file size.
all_sizes_lin = [1+n for n in range(n_bench)]
print(len(all_sizes_lin) == len(all_sizes_small))
print(all([size_lin == size_small for size_lin, size_small in zip(all_sizes_lin, all_sizes_small)]))
True
False
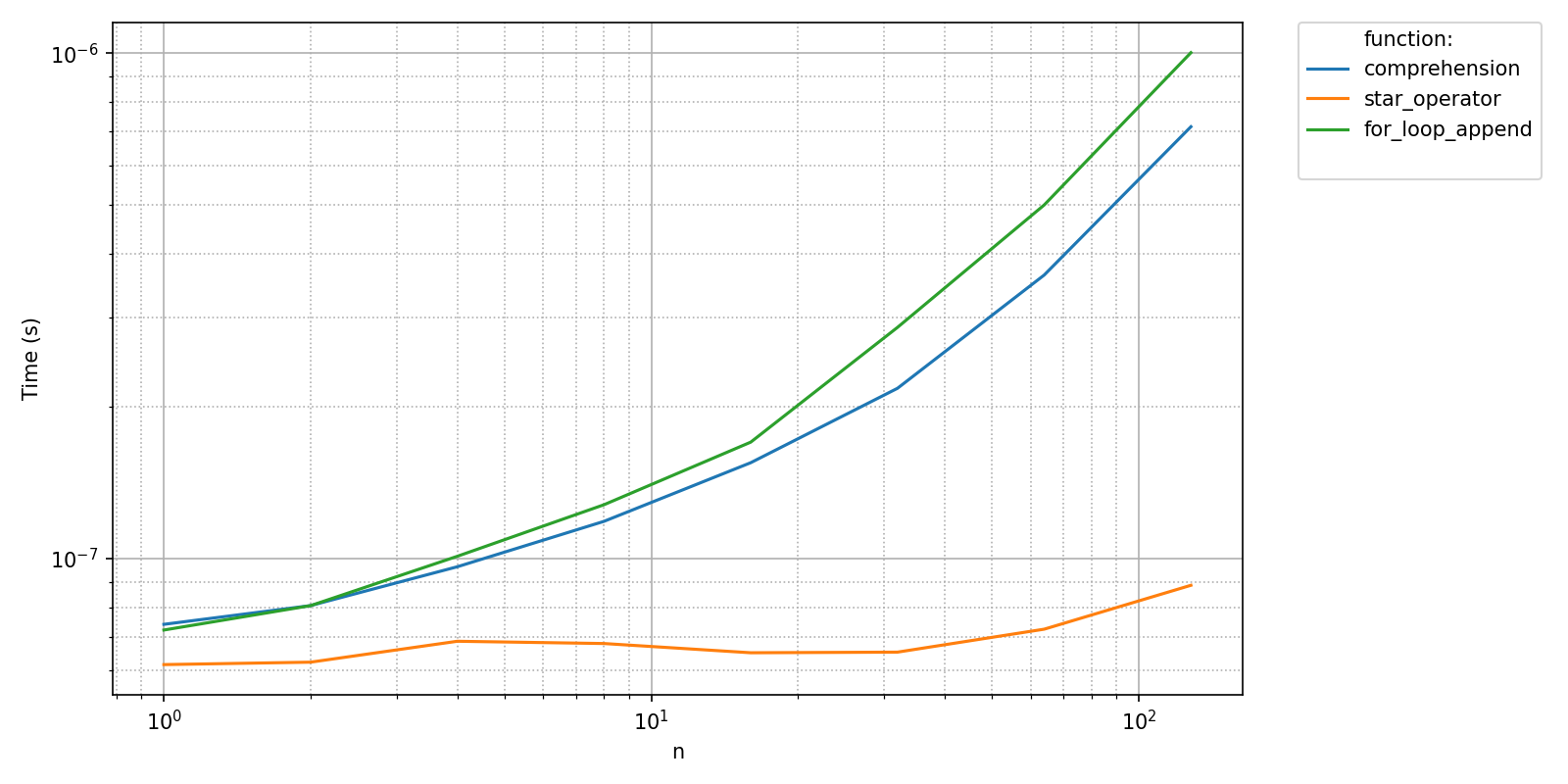
Hence, the following will not trigger a new benchmark although it should, as the sizes are not stored in the *.npy benchmark file. As a consequence, the following plot is inaccurate.
pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes_lin ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
show = True ,
)
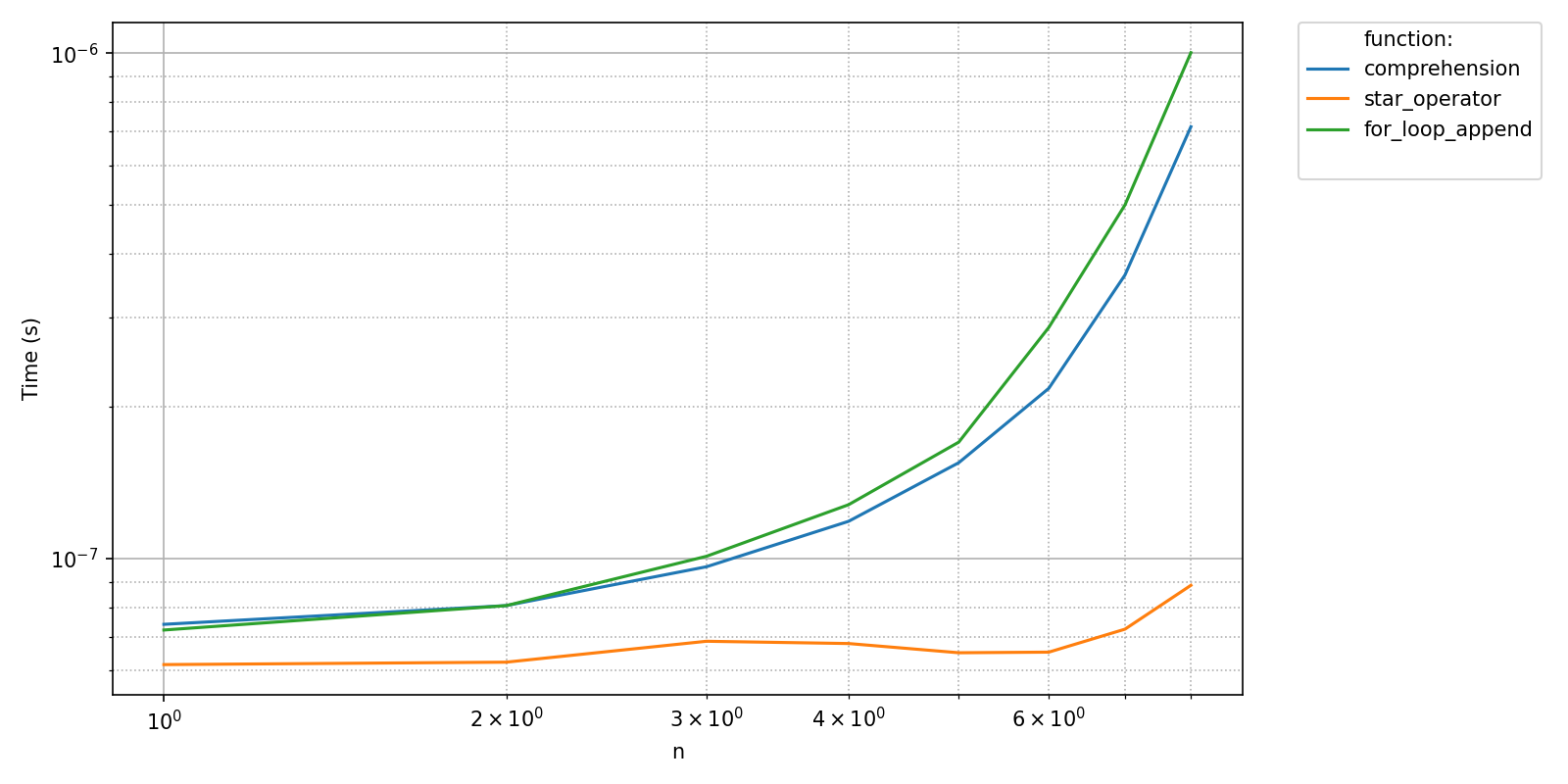
Using a *.npz file as an output allows pyquickbench.run_benchmark() to detect this change. For instance, both outputs here are correct.
timings_filename = "My_benchmark_file.npz"
pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes_small ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
show = True ,
)
pyquickbench.run_benchmark(
all_sizes_lin ,
all_funs ,
filename = timings_filename ,
show = True ,
)