Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Benchmark of Error-Free Transforms for summation#
This benchmark compares accuracy and efficiency of several summation algorithms in floating point arithmetics
def naive_sum(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,0)
def np_sum(x):
return np.sum(x)
def m_fsum(x):
return m.fsum(x)
def SumK_1(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,1)
def SumK_2(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,2)
def SumK_3(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,3)
def SumK_4(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,4)
def SumK_5(x):
return choreo.segm.cython.eft_lib.SumK(x,5)
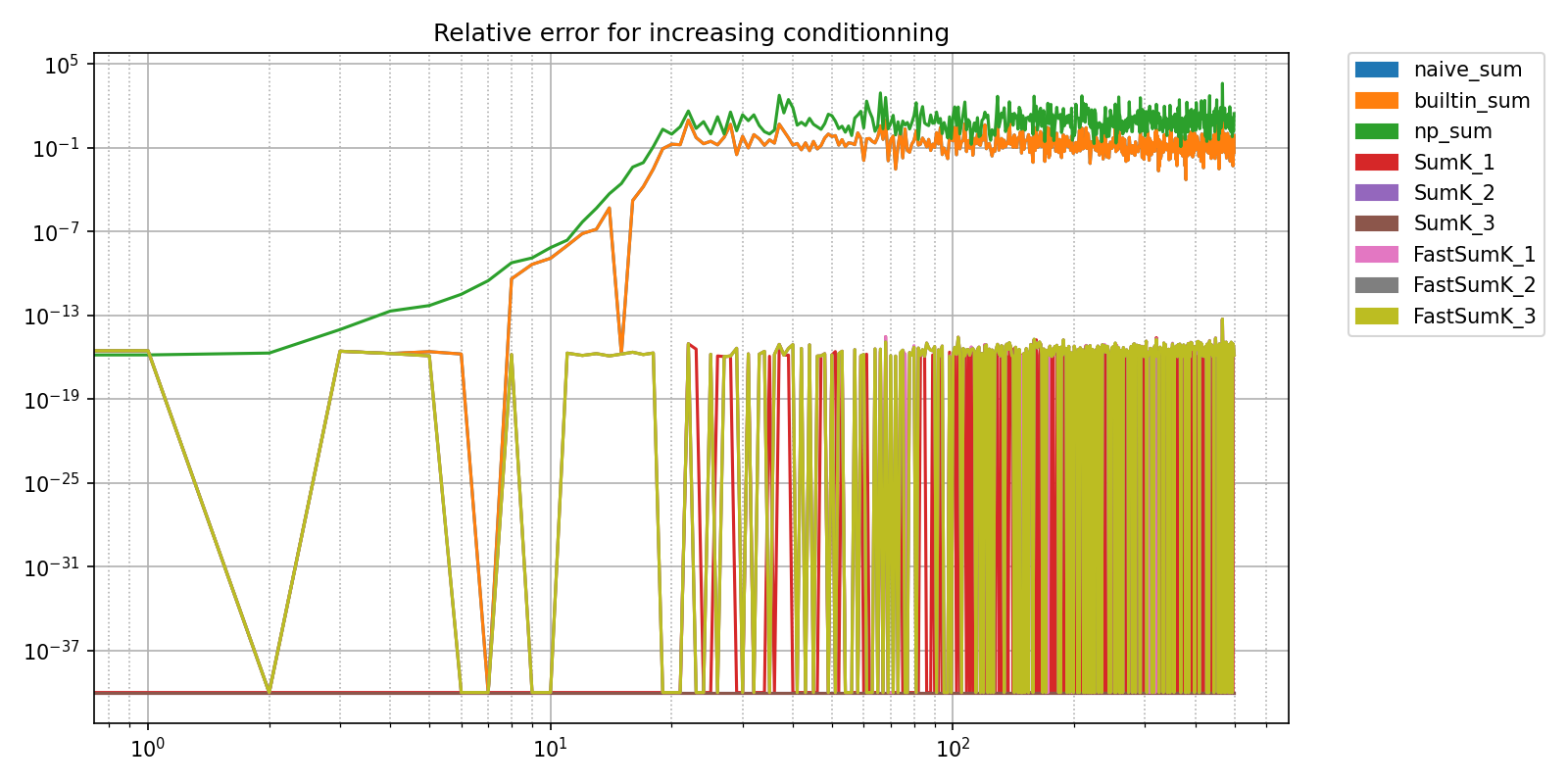
def prepare_x(n):
x = np.random.random(n)
return {'x': x}
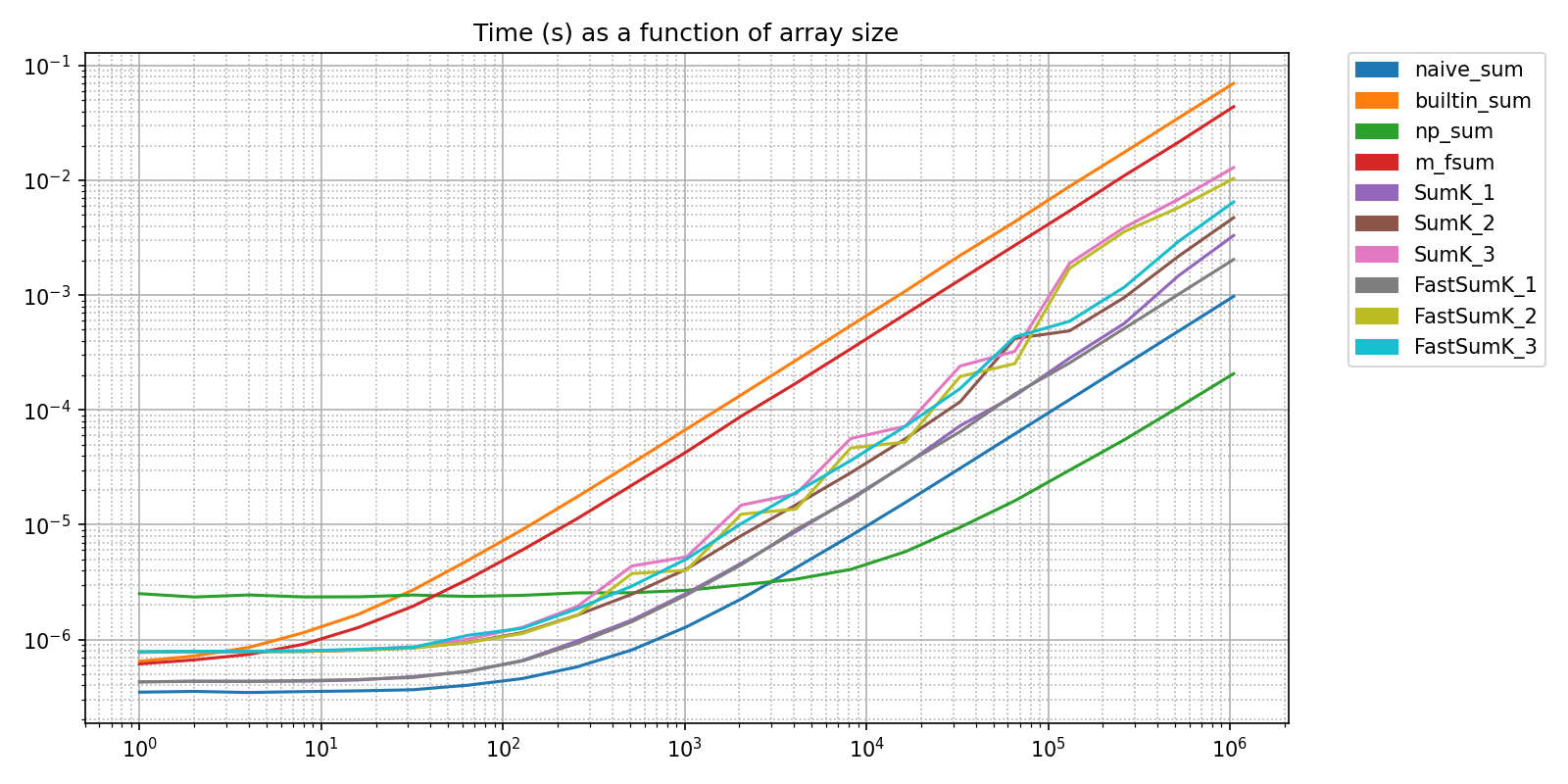
pyquickbench.plot_benchmark(
all_times ,
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
show = True ,
title = "Measured CPU time" ,
)
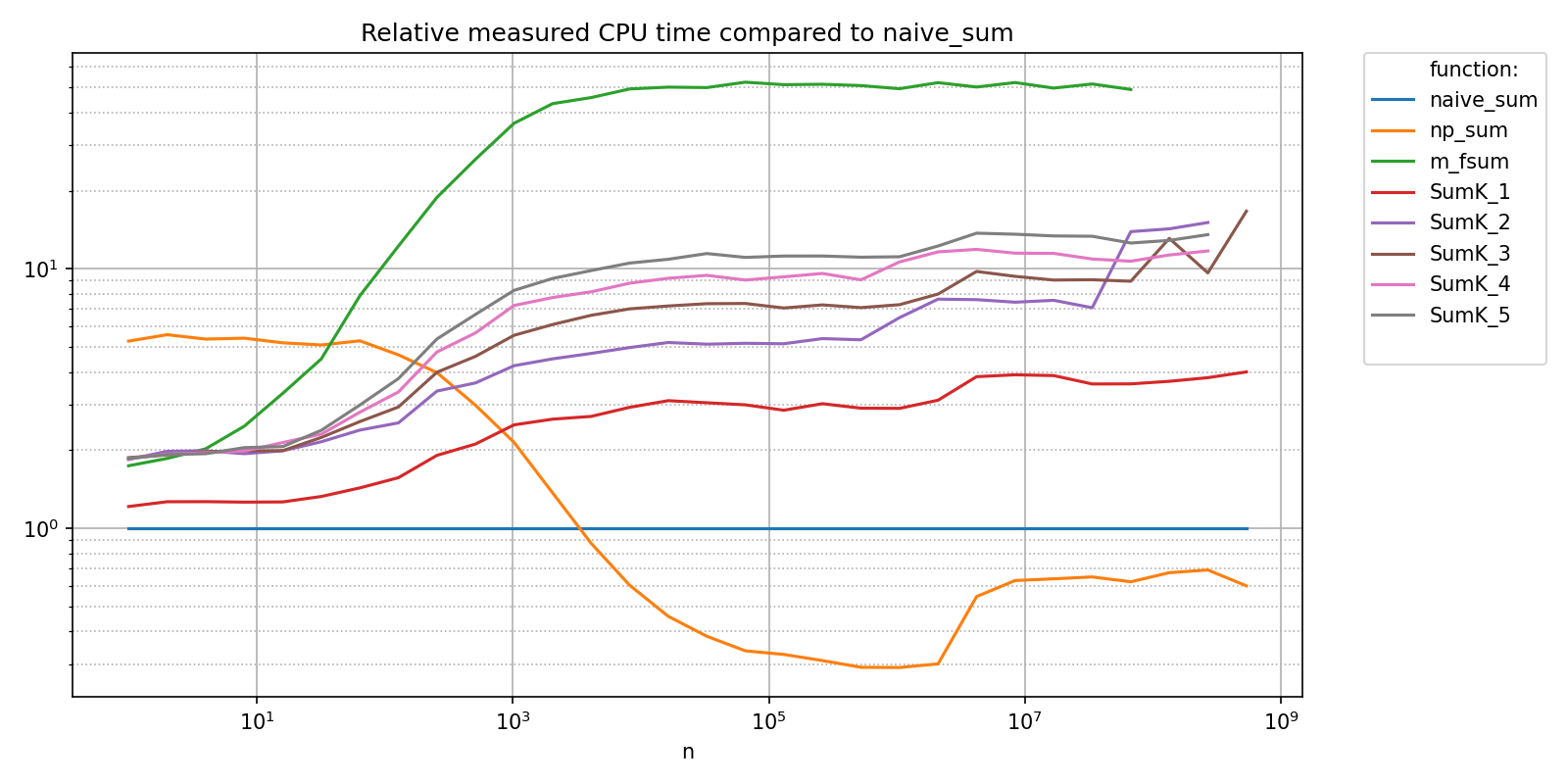
pyquickbench.plot_benchmark(
all_times ,
all_sizes ,
all_funs ,
show = True ,
relative_to_val = {pyquickbench.fun_ax_name: "naive_sum"},
title = "Relative measured CPU time compared to naive_sum" ,
)